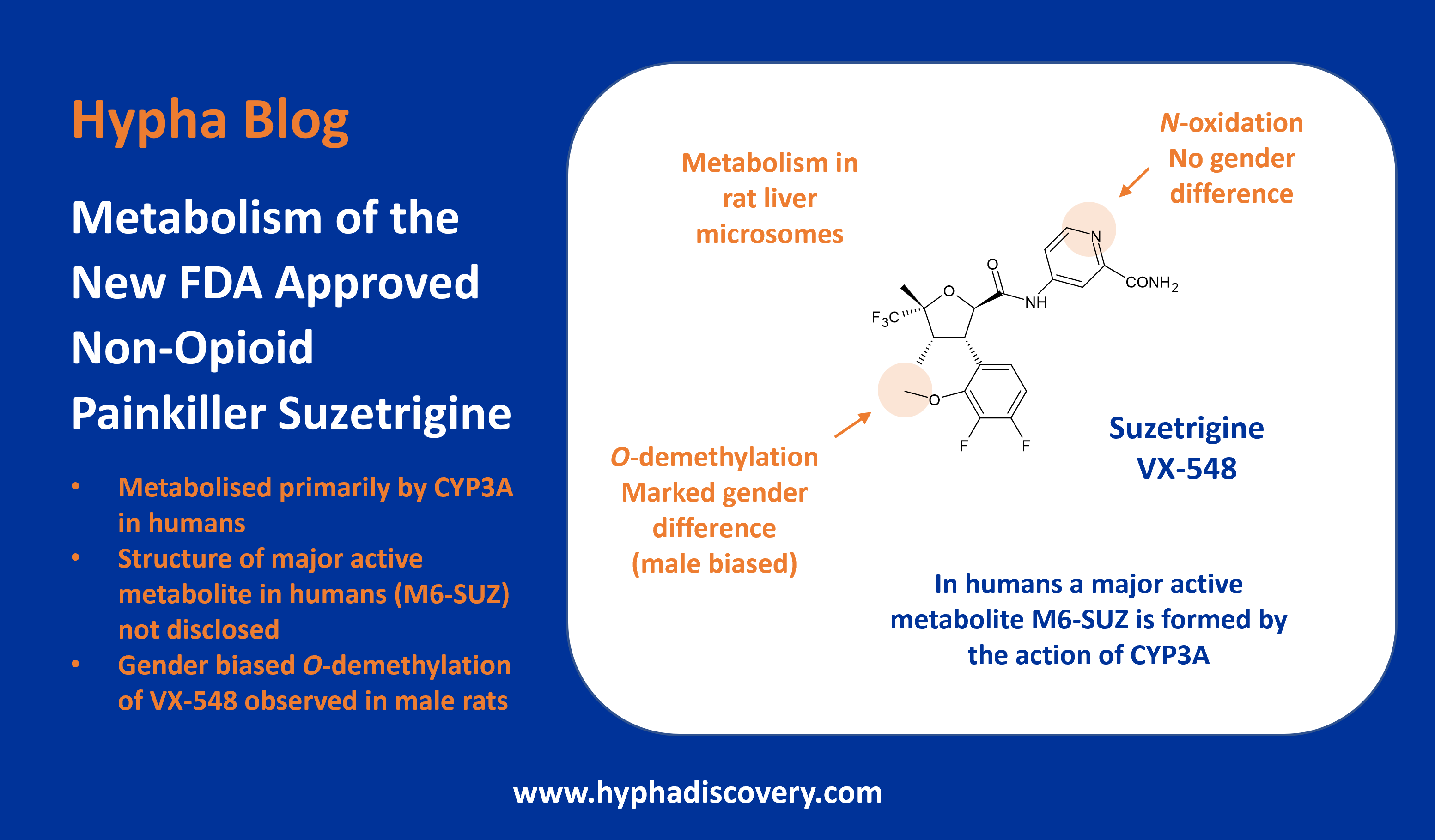
Oxidative biotransformation of elinzanetant to 3 active metabolites
Elinzanetant is a dual neurokinin-1,3 receptor antagonist under development for treatment of menopausal vasomotor symptoms such as hot flashes and associated sleep disturbances.
Human mass balance study
Elinzanetant is extensively oxidised to several metabolites in vivo. Three of these are circulating active metabolites which have similar pharmacological activity to the parent drug, and may contribute to the overall efficacy.
In the human radiolabelled mass balance study, although the parent drug was the main circulating species (39% total radioactivity), three oxidised metabolites were present at 7.6% (M27), 13.7% (M30/34) and 4.9% (M18/21) of total radioactivity. Due to its exposure of >10% AUC in plasma, M30/34 is considered a major (although not disproportionate) human metabolite. All three metabolites were assessed for safety in animals and in clinical studies.
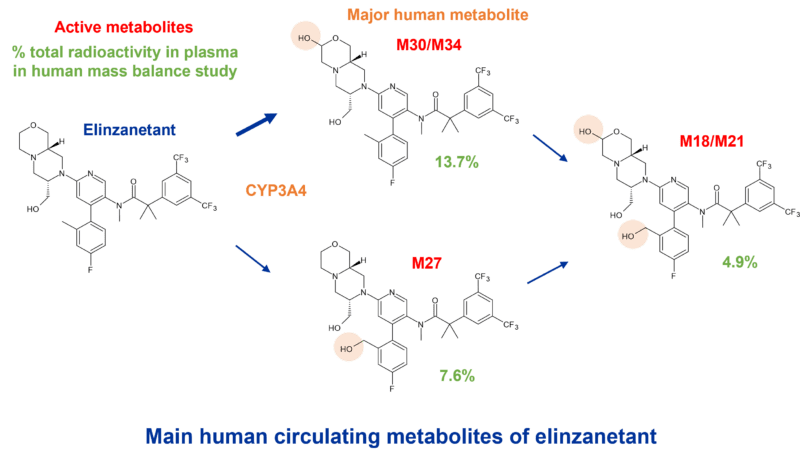
M30/34 is formed by hydroxylation of the morpholine ring to a hemiacetal which interconverts between its diastereomeric forms. The other main circulating metabolites arise from hydroxylation of the aromatic methyl group (M27) and double oxidation at these two susceptible positions to an interconverting secondary metabolite (M18/21).
M30/34 is also the major metabolite formed in human hepatocytes and human liver microsomes, with dehydrogenated and morpholine ring-opened metabolites also reported. Through use of the inhibitor cobicistat, studies showed that CYP3A4 is primarily responsible for elinzanetant’s clearance, with a minor contribution by O-glucuronidation.
Excretion through faeces
 The drug is primarily excreted through faeces and was shown to be stable in a faecal microbial environment under anaerobic conditions. There was a rather large and unexplained range reported for unchanged drug in faeces, although most of the metabolites present could be assigned to already known structures. Main metabolites seemed to stem from morpholine ring opening reactions such as M17 via M30/34.
The drug is primarily excreted through faeces and was shown to be stable in a faecal microbial environment under anaerobic conditions. There was a rather large and unexplained range reported for unchanged drug in faeces, although most of the metabolites present could be assigned to already known structures. Main metabolites seemed to stem from morpholine ring opening reactions such as M17 via M30/34.
Paper
Schulz, S. I., Schultze-Mosgau, M. H., Engelen, A., Singh, N., Pawsey, S., Francke, K., Lock, R., & Rottmann, A. (2025). Mass Balance Recovery, Absorption, Metabolism, and Excretion of Elinzanetant in Healthy Human Volunteers and in vitro Biotransformation. European journal of drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics, 50(1), 91–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-024-00930-3